Gillette Stories
Gillette Stories
At Gillette Children's we help every child in our care live a life defined by dreams, not diagnosis. Here you will find stories of inspiration and triumph and joy. Learn more about our work with patients and families that don't give up as we help every child live their story. Gillette Stories Magazine


For Some Families, Rare Diseases Aren’t Rare
Gillette Children’s Highlights Community, Expertise Ahead of Rare Disease Day
Read More
Legg-Calve-Perthes Disease
A Maze of Symptoms Leads to Perthes Disease Diagnosis
Read More
Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy
“We’ve Got This”: A Rare Disease Diagnosis and Treatment Journey
Read More
Cerebral Palsy
Better Together: Benny’s Journey with Animal-Assisted Therapy
Benny now walks farther, stronger, and more confidently than ever through animal-assisted therapy at Gillette.
Read More
Innovation and Research
Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation: Inpatient vs. Outpatient
Learn about the differences between inpatient and outpatient pediatric rehabilitation.
Read More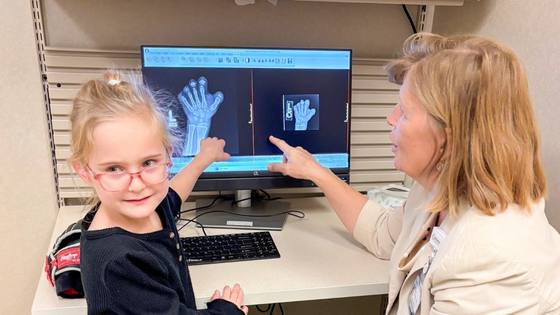
Amniotic Band Syndrome
Gillette Children’s Advocacy Helps Secure Sports Prosthetics
Read MoreHoliday gift guide for children and adults who have disabilities
Read More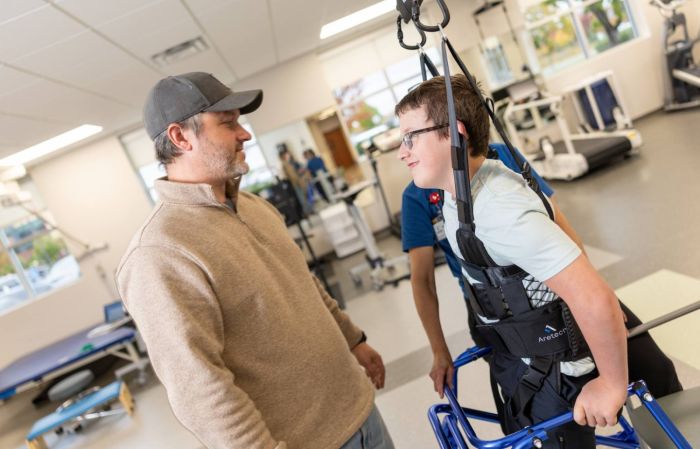
Cerebral Palsy
Family Grateful for Gillette Children’s Inpatient Rehabilitation
John needed the time and space for rehabilitation following a complex surgery for his cerebral palsy. Gillette Children's Inpatient Rehabilitation Unit was there to support John every step of the way.
Read More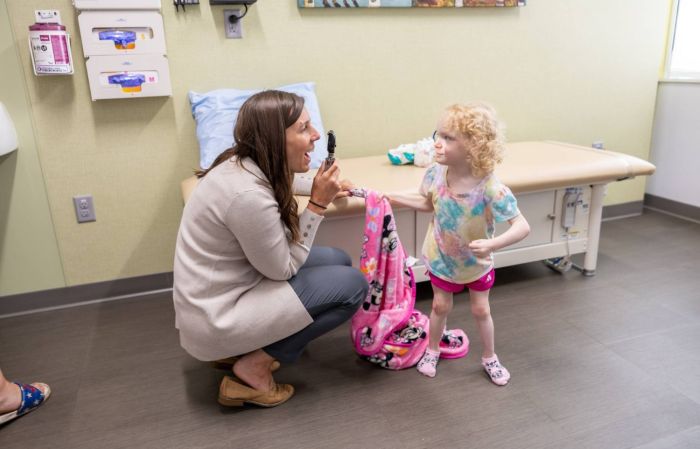
Our Team
My Child Needs a Complex Care Appointment. What’s Next?
At Gillette Children’s, we focus on coordinating care for children and young adults who have chronic and complex medical conditions.
Read MoreHealth Library
Find education related to your condition, procedure, care at home, and more.
Search Health LibraryResearch
Gillette Research aims to improve treatment options for children who have disabilities.
Explore Gillette ResearchNews
From innovations to innovators, Gillette Children’s shares our news as leaders in specialty care and research.
News Releases Home Page
Home Page
